Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of welding technologies, precision and innovation take center stage. Laser welding, particularly with IPG LightWELD, introduces a revolutionary approach to magnet welding using photons, a game-changer in comparison to traditional methods like TIG and MIG. This blog delves into the intricacies of laser welding magnets, shedding light on how the use of photons, impervious to magnetic fields, sets IPG LightWELD apart.
Understanding the Basics:
Before we delve into the advantages of IPG LightWELD in magnet welding, let’s briefly understand the conventional methods. Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) and Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding have long been the go-to methods for joining magnets. However, these techniques come with inherent challenges, particularly when working with materials sensitive to magnetic fields.
The Photon Advantage:
IPG LightWELD utilizes photons, the particles of light, for welding. Unlike electrons used in TIG and MIG welding, photons are not influenced by magnetic fields. This key distinction allows for unparalleled precision and control, especially when working with magnetic materials.
“Magnets have revolutionized the landscape of high-power laser beam welding, significantly enhancing weld quality in critical metal structures. The BAM German Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing, leveraging COMSOL Multiphysics, successfully applied a stationary magnetic field to counteract challenges like the Marangoni effect, resulting in a more homogeneous and desirable V-shaped weld. This breakthrough, validated through actual welds, addresses issues of spattering, droplet ejection, and non-uniformities, offering a promising solution for industries such as shipbuilding and reactor vessels. COMSOL Multiphysics played a pivotal role in navigating the complexities of the welding process, providing a user-friendly interface and adaptable modules. This innovative approach has the potential to redefine high-power laser beam welding, ensuring impeccable welds and reinforcing the reliability of metal structures across diverse applications.” – Said Bruno Carvalho laser welding specialist at Spark & Co inc.
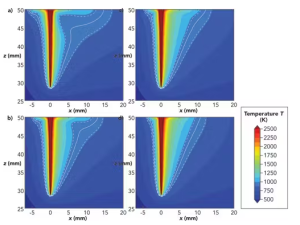
The Marangoni effect, causing non-uniform welds, is a key challenge addressed by the magnetic field. Without external forces, a typical weld assumes a wine-glass shape (Fig a and b left), resulting in stresses and distortions. However, when a static magnetic field is applied (Fig a and b right), the weld takes on a more homogeneous, V-shaped form, aligning better with the desired outcome.
- Precision in Magnet Welding:
– Electrons in TIG and MIG welding can be affected by magnetic fields, leading to inconsistencies in the welding process.
– IPG LightWELD’s photon-based approach ensures precise control, producing clean and accurate welds on magnetized materials without the interference of magnetic fields.
- Reduced Heat Affected Zone (HAZ):
– Traditional methods may result in a larger Heat Affected Zone, affecting the magnetic properties of the material.
– IPG LightWELD’s photon beam generates minimal heat, reducing the HAZ and preserving the integrity of the magnetic material.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Speed:
– Electron beam welding can be a slow process, and TIG/MIG welding may require additional post-weld processing.
– IPG LightWELD’s rapid and precise photon-based welding streamlines the process, saving time and increasing overall efficiency.
- Versatility in Magnet Types:
– Magnets come in various forms and materials, each with its unique characteristics.
– IPG LightWELD’s photon welding offers versatility, allowing for the welding of different magnet types without compromising on quality.

Conclusion:
As industries continue to demand higher precision and efficiency in magnet welding, the use of IPG LightWELD with photon technology emerges as a transformative solution. The ability to weld magnets with unparalleled precision, free from the constraints of magnetic interference, positions IPG LightWELD at the forefront of welding innovation. As we move towards a future where precision meets efficiency, photon-based welding technologies undoubtedly pave the way for groundbreaking advancements in the field.
Other articles on the subject :
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1875389212025412
https://www.sme.org/technologies/articles/2019/october/traditional-versus-laser-welding/
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adem.202200682